Mendel observed that the pea plants' traits were often similar to those of their parents. Sometimes, however, the pea plants had different traits than their parents. Mendel experimented with thousands of pea plants to understand the process of heredity. Mendel's work formed the foundation of genetics, the scientific study of heredity. Mendel's experiments changed the general
perception of heritable variants from ephemeral
and blendable to discreet entities passed from
parents to offspring, present even though they
are not always visible.
2. Draw the structure of DNA and who discovered this structure.
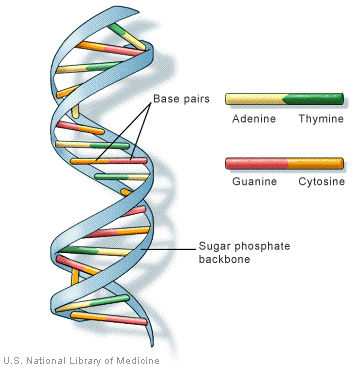
James Watson, Francis Crick, Maurice Wilkins
3. Explain each of the five examples of variations that occur to DNA and give an example of each.
Gene copy number - chimpanzees
point mutation - whipped dogs
insertion - pea plants
Inversion - flipping of large segments of DNA within a chromosome
Repitition - repetitions like those that underlie forensic DNA tests
4. What is evo-devo? A subspecialty ithin
evolutionary biology that has come to be known
as evo-devo Concentrates on studying the effects
of changes in important developmental genes
and the role they play in evolution.
5. Make a connection between human migration and the mutation of lactose intolerance.
Lactose-tolerant population started with a little population then later the populations have differ-
ent mutations in the key region-a striking ex-
ample of the repeated evolution of a similar trait
by independent changes affecting one gene.
No comments:
Post a Comment