Elements: matter combined with same atoms with same proton numbers
Compound: mixture of elements
Atom: "the undivisible", smallest division of anything
Proton: part of the nucleus of an atom, with a positive +1 charge and weighing 1 Dalton
Neutron: other part of the nucleus of an atom, with no charge, also weighing 1 Dalton
Electron: particles that surround the nucleus, with a negative -1 charge, with a negligible weight
Isotope: When an atom has different number of neutrons-
Atoms
Atoms are the basic material of everything, and it can be divided into 3 sub-atomic particles: protons, electrons, and neutrons. Below is a diagram of the carbon atom

As seen in the diagram, electrons are found on the outer energy level of the nucleus while protons and neutrons are found inside the nucleus.
Electrons are arranged according to their energy level. This is called the electronic structure orelectronic configuration of the atom. Shown Below:

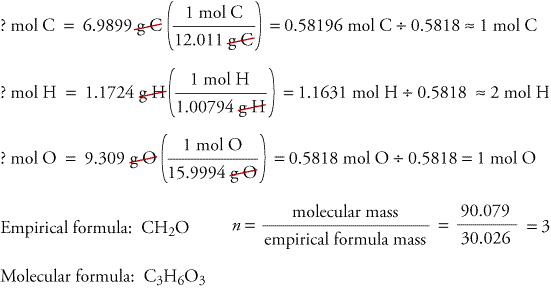
Electrons are transferred in ionic bonds. Ionic bonds form when metals bond with non metals. Salts are examples. Like other ionic compounds, many salts are soluble in water. In water, the giant 3-D lattice breaks up into ions which move around relatively freely in solution. Each ion is surrounded by a cluster of water molecules (we say they are hydrated). This can be shown by an equation:
Atoms
Atoms are the basic material of everything, and it can be divided into 3 sub-atomic particles: protons, electrons, and neutrons. Below is a diagram of the carbon atom

As seen in the diagram, electrons are found on the outer energy level of the nucleus while protons and neutrons are found inside the nucleus.
| Particle | Location | Relative mass | Charge |
| Proton | Nucleus | 1 | +1 |
| Neutron | Nucleus | 1 | 0 |
| Electron | Outside the nucleus | 1/1840 | -1 |
Electrons are arranged according to their energy level. This is called the electronic structure orelectronic configuration of the atom. Shown Below:

Elements
Elements are substances made out of atoms with the same number of protons. They are the most basic substance.
Each element has its own:
- name and chemical symbol
- characteristic physical properties, e.g. density, electrical conductivity, melting point and boiling point
- characteristic chemical properties, e.g. reactions with water, oxygen, acids and other chemical
Different number of neutrons = an isotope
Different number of electrons = an ion
Different number of protons = different element
Compounds
Compounds are formed by combining elements through chemical reactions. However, elements can only bond according to the number of valence electrons they have, and they always try to to get 8 valence electrons, aka the octet rule.
Usually you would try to derive the empirical formula from the molecular formula. The empirical formula is the same thing as the molecular formula except you take the L.C.M of the formula and simplify it. In other words, the molecular formula gives you exact number of atoms while empirical formula only gives you the ratio. Example Problem:
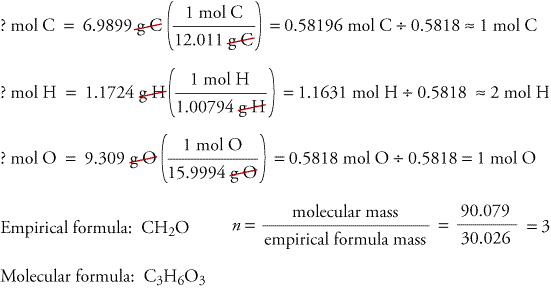
Chemical Bonds
Chemical bonds are something that atoms form with each other when combining with each other. There are 2 kinds of chemical bonds, the Ionic Bond, and the Molecular Bond (Covelant Bond).
Ionic Bonds
NaCl (s) + aq  Na+ (aq) and Cl- (aq)
Na+ (aq) and Cl- (aq)
Covalent Bonds (Molecular Bonds)
Electrons are transferred in covelant bonds. Covalent bonds form when when non metals bond with non metals.
For our second class of honors biology, we went through some worksheets of basic chemistry, in preparation for our topic on biochemistry. The above information gives a general idea of what I learnt/ reviewed in the class. In addition to that, we reviewed on how to correctly draw lewis-dot structures for ionic bonds and covelant bonds respectively.
No comments:
Post a Comment